The key to penicillin allergy delabeling
How Are Antibiotic Allergies Classified?
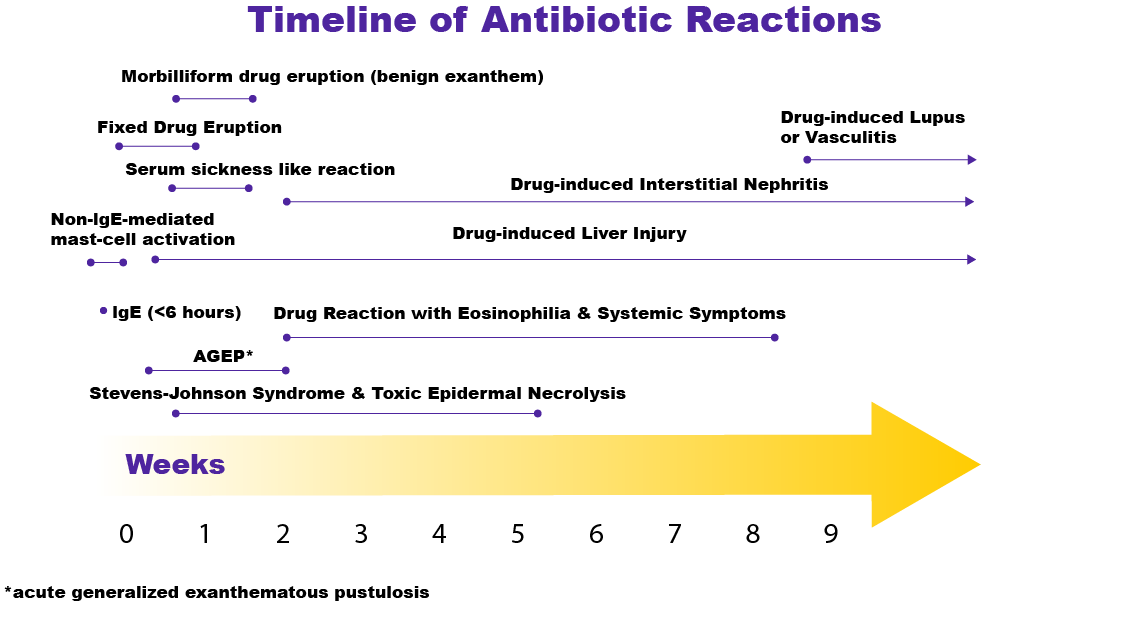
Allergic drug reactions can be classified based on chronology, mechanism, and clinical phenotypes. The chronology of drug allergic reactions is generally simplified into either immediate or delayed reactions.
Immediate Reactions:
- Occur within 1 hour but in some cases ≤ 6 hours of exposure to the drug.
- Phenotypic reactions:
Urticaria
Angioedema
Bronchospasm
Anaphylaxis
- Often Ig-E mediated
Delayed Reactions:
- Evolve over days, or in some cases, weeks following exposure to the drug.
- Most common clinical phenotype is a benign (e.g., morbilliform drug eruption) exanthem.
- More severe delayed reactions include:
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs)
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (STS)
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)
- Other more severe delayed reactions:
Serum sickness-like reactions (SSLRs)
SSLRs are characterized by urticaria-like (lesions persist > 24 hours) and erythema multiforme-like lesions, joint inflammation and fever, but unlike serum sickness, nephrotoxicity, and hypocomplementemia are rare.
The immunologic mechanisms for these delayed reactions are likely related to drug-specific T cells including Th1, Th2, and cytotoxic T cells.
- Organ-specific delayed drug reaction phenotypes (often without cutaneous manifestations)
Cytopenias - neutropenia/leukopenia/anemia
Liver injury
Interstitial nephritis
Vasculitis
The chronology of various drug reactions is shown below.